With the development of the national economy and the improvement of the voltage level of urban power supply, cross-linked polyethylene insulated power cables (XLPE) have been increasingly widely used at home and abroad due to their reasonable process and structure, excellent electrical performance, and safe and reliable operating characteristics. Especially in the field of high-voltage transmission, significant progress has been made. Compared with oil filled cables, cross-linked cables are easy to lay and install, have simple operation and maintenance, and do not have oil leakage problems. However, recent operations and research have shown that the insulation of cross-linked polyethylene cables is prone to dendritic discharge during operation, causing insulation aging and damage, seriously affecting the service life of cross-linked polyethylene insulated power cables. Therefore, fully understanding the insulation characteristics of cross-linked cables, timely and effectively discovering and preventing certain defects in insulation, is of great significance for ensuring the safe operation of equipment and even systems. The main factors affecting the insulation of cross-linked cables and the principle of cable handover tests were elaborated, and it was believed that it is necessary and feasible to conduct AC withstand voltage tests on cross-linked cables on site.
In order to ensure the safe and reliable operation of cables, relevant international standards have made clear provisions for various tests of cables. The main test items include measuring insulation resistance, DC withstand voltage, and leakage current. The measurement of insulation resistance is mainly used to check whether the cable insulation is aging, damp, and exposed insulation defects during the withstand voltage test. The DC withstand voltage and leakage current tests are conducted synchronously, with the aim of discovering defects in the insulation. However, in recent years, domestic and international experiments and operational experience have proven that DC withstand voltage tests cannot effectively detect insulation defects in cross-linked cables, and may even cause insulation hazards in cables. From 1978 to 1980, the German company Sechiswag experienced 87 faults in XLPE cables with a voltage level of 10 kV in 41 circuits; XLPE cables with voltage levels of 3 kV to 24.5 kV in Sweden have been put into operation for over 9000 km and have experienced 107 failures. There have also been multiple cable accidents in China, and a considerable number of cable failures are caused by the negative effects of frequent DC withstand voltage tests. Therefore, relevant departments at home and abroad widely recommend using AC withstand voltage instead of traditional DC withstand voltage.
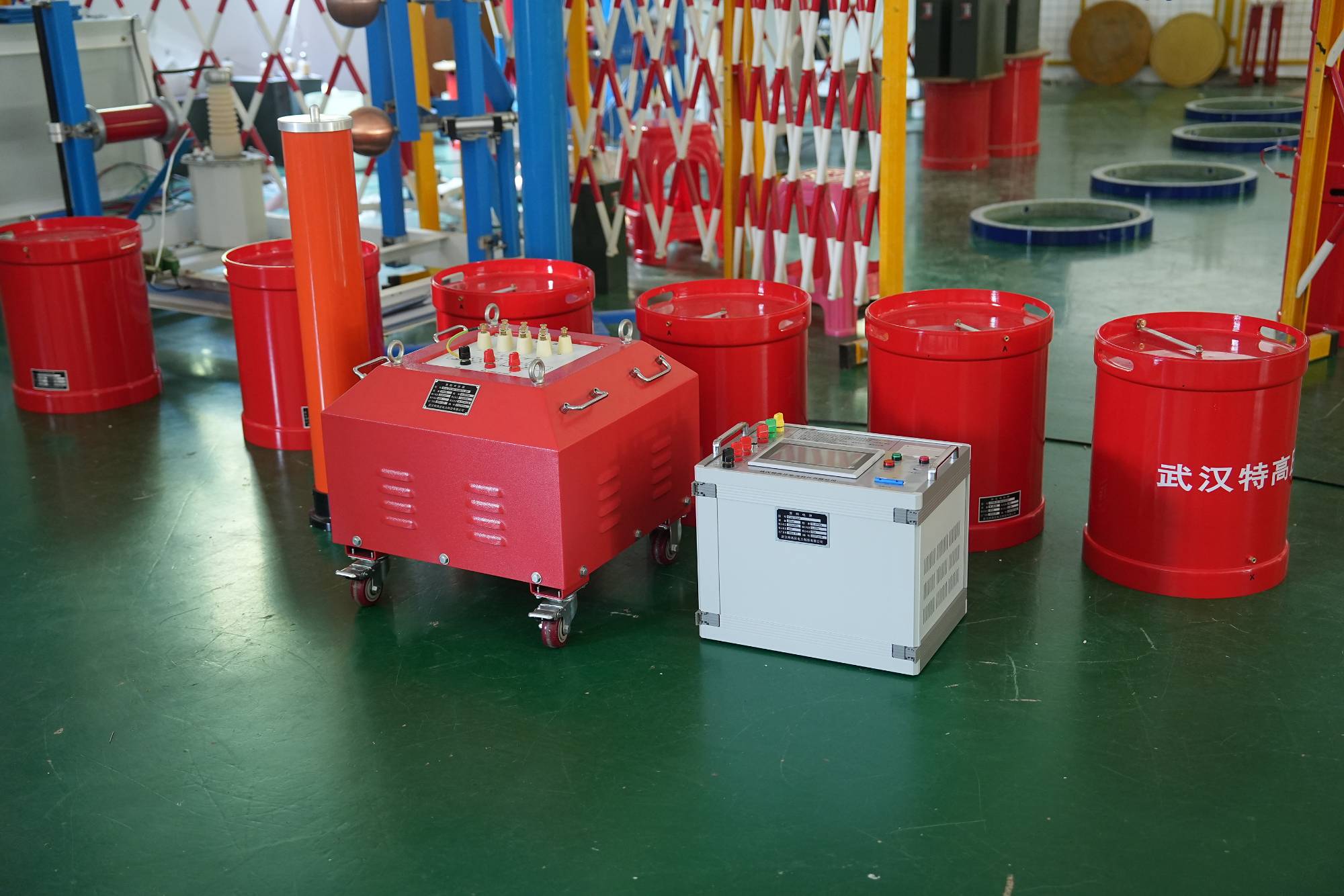
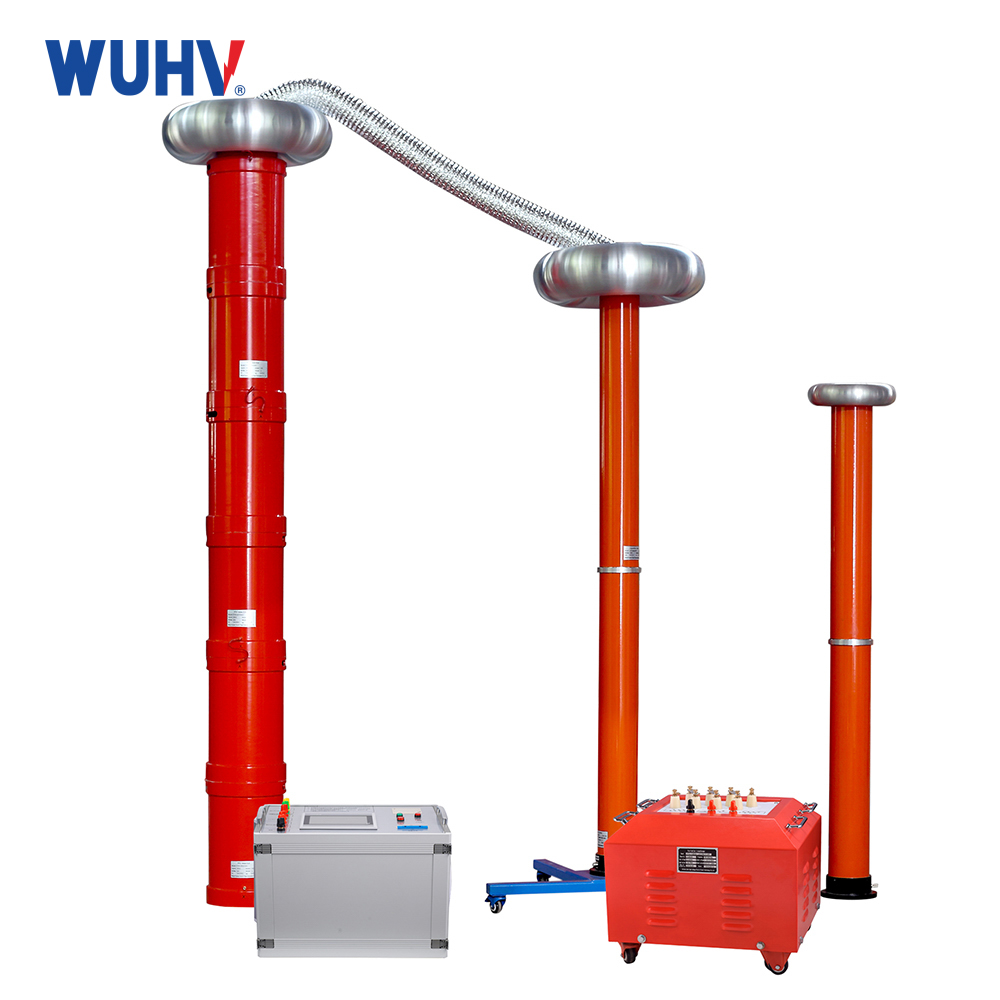
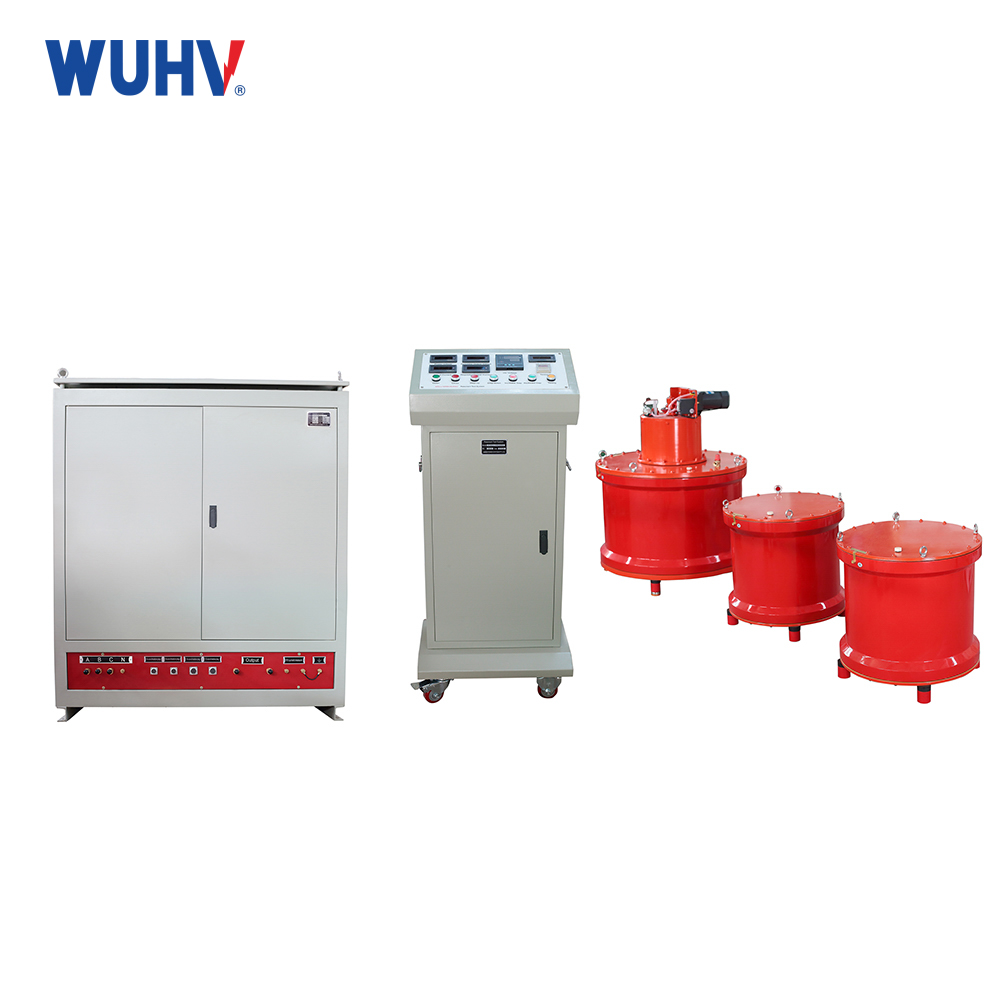
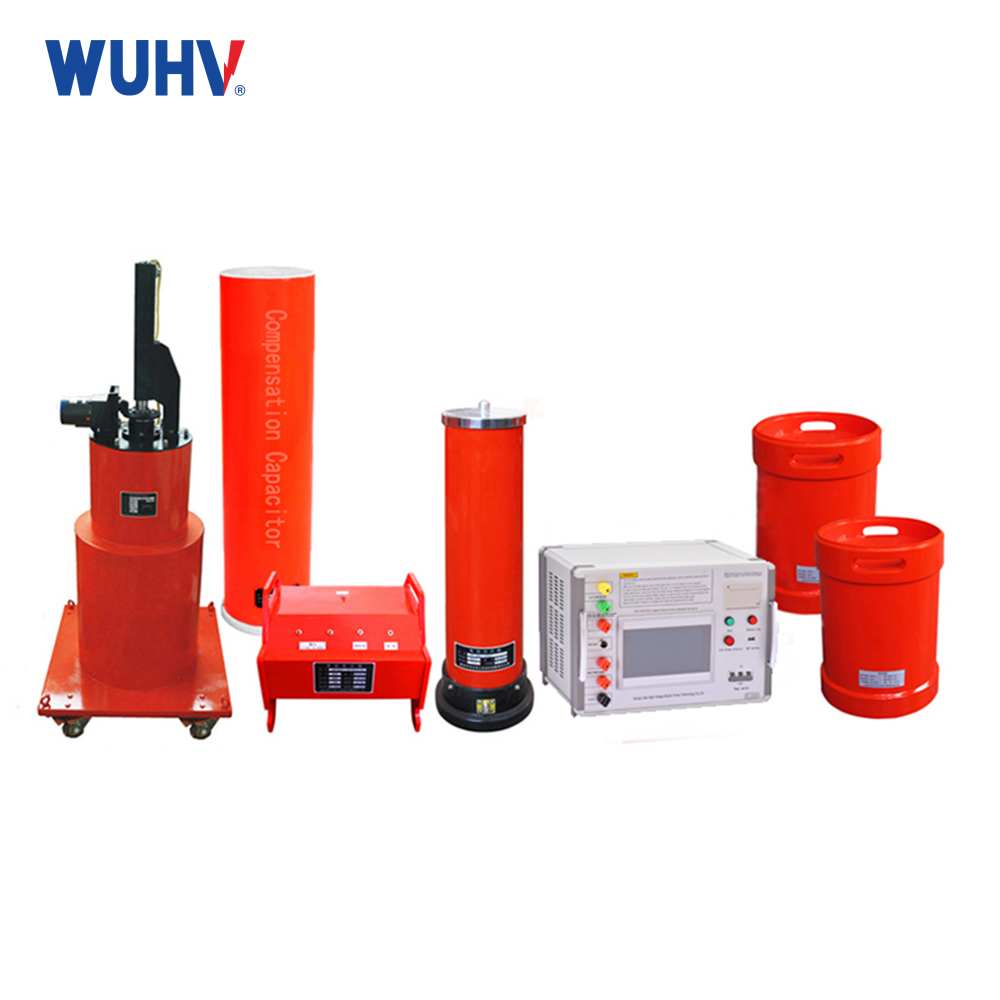
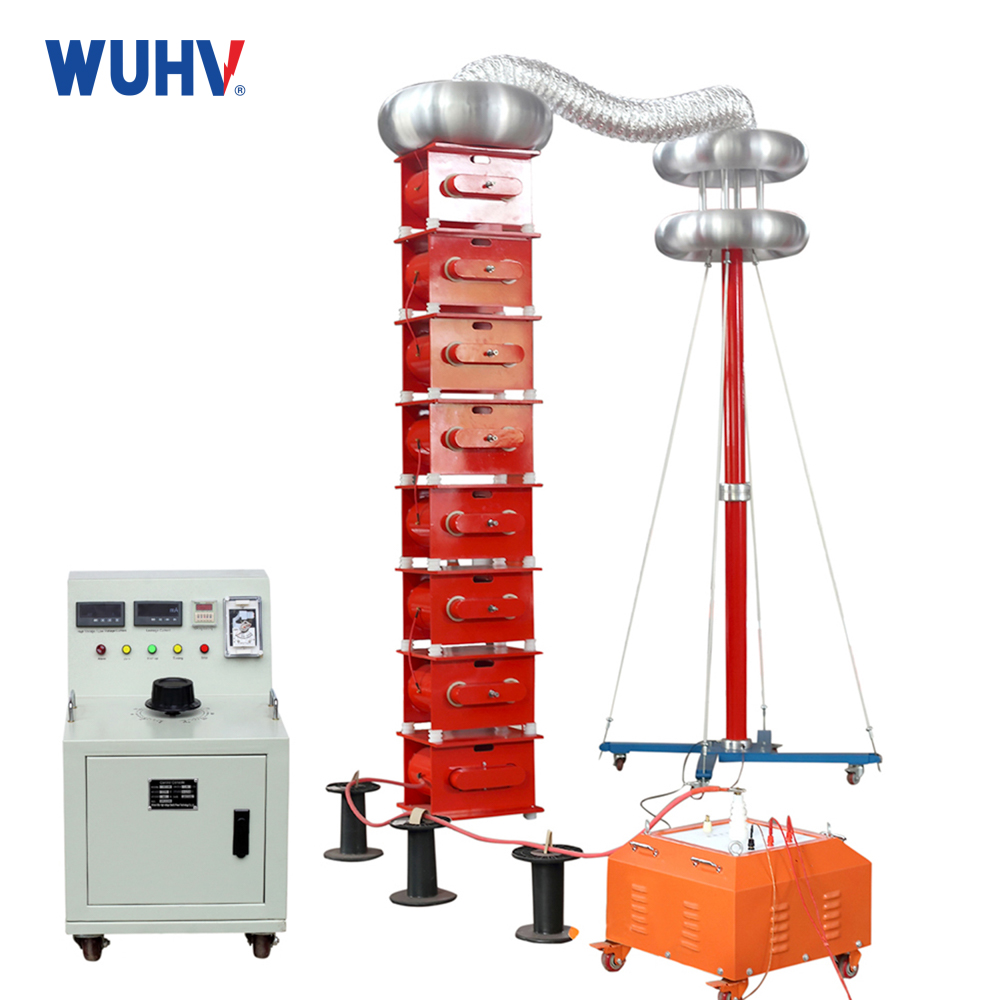
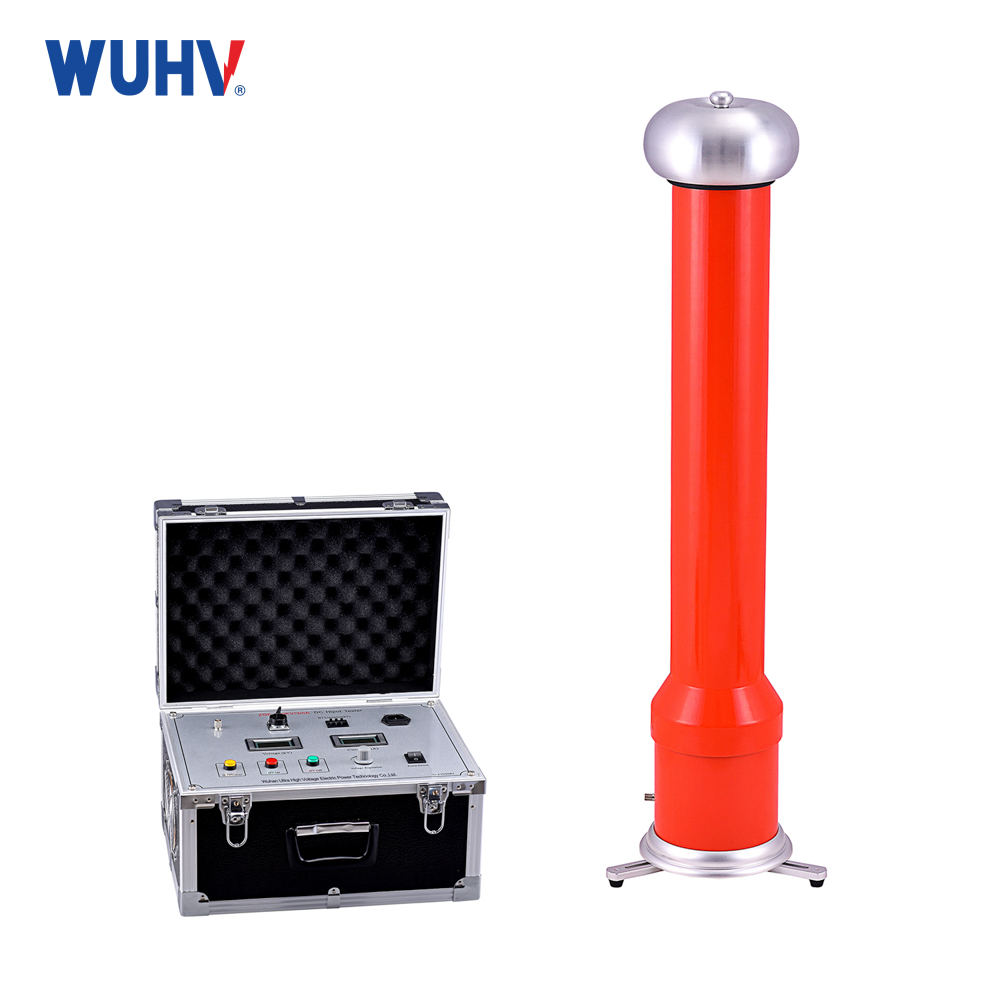
The variable frequency series resonance test devicedeveloped and produced by Wuhan UHV Power is based on the principle of series resonance. It uses an excitation transformer to excite the series resonance circuit, adjusts the output frequency of the variable frequency controller, and causes the circuit inductance L and the test sample C to resonate in series. The resonant voltage is the voltage applied to the test sample. This product is suitable for AC withstand voltage testing of 10KV, 35KV, 110KV, 220KV, and 500KV polyethylene power cables; Suitable for 60KV, 220KV, 500KV GIS AC withstand voltage test; Suitable for power frequency withstand voltage testing of large transformers and generator sets; Induction withstand voltage test for power transformers; High voltage withstand tests such as grounding resistance measurement have a wide range of applications. Automatic and manual tuning, quickly finding the resonance point, high stability and reliability, user-friendly human-machine interface, making it very convenient for conducting AC withstand voltage tests in industries such as power systems, metallurgy, petroleum, and chemical engineering