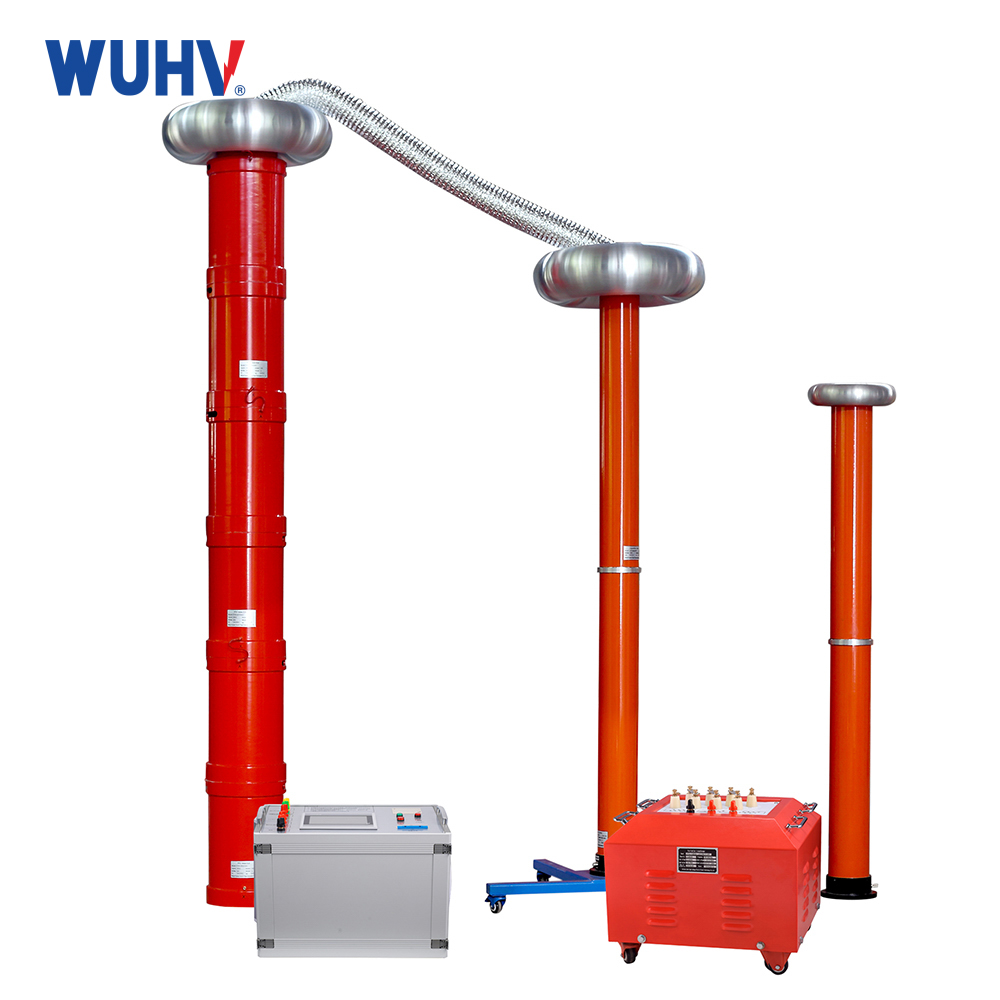
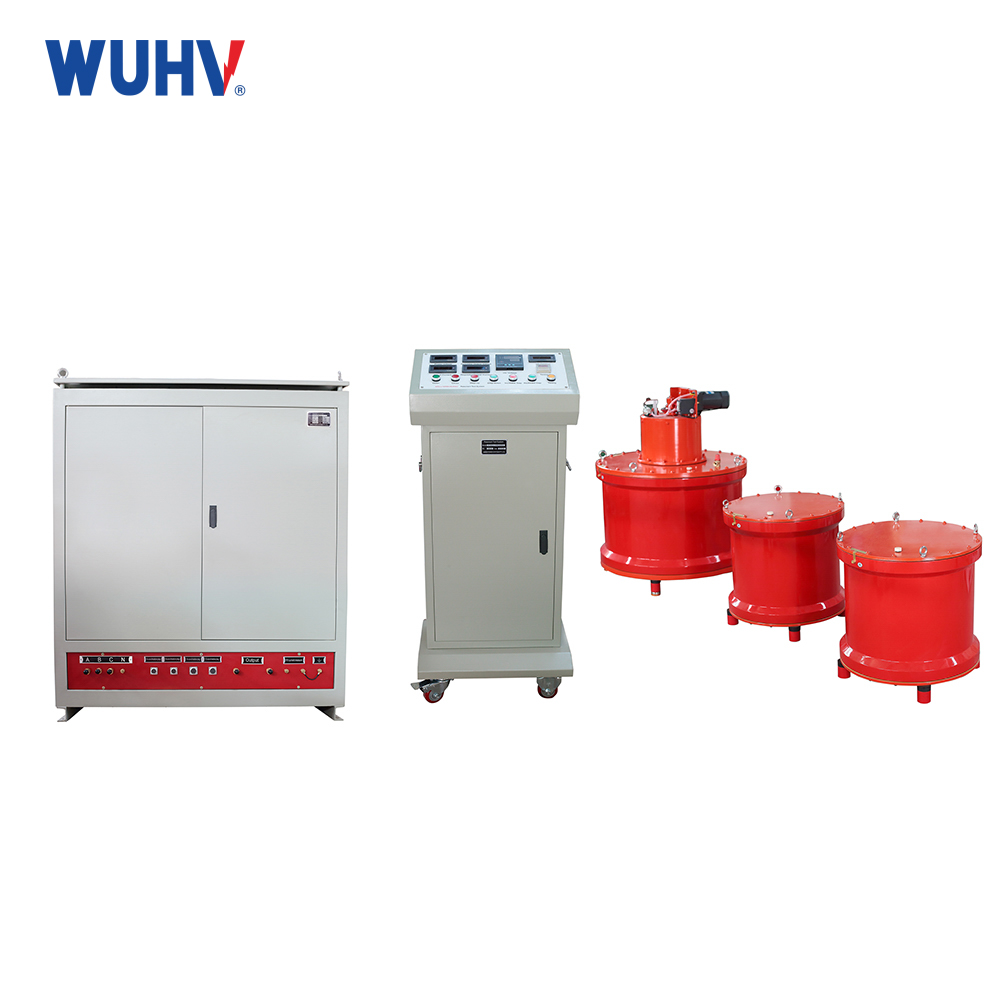
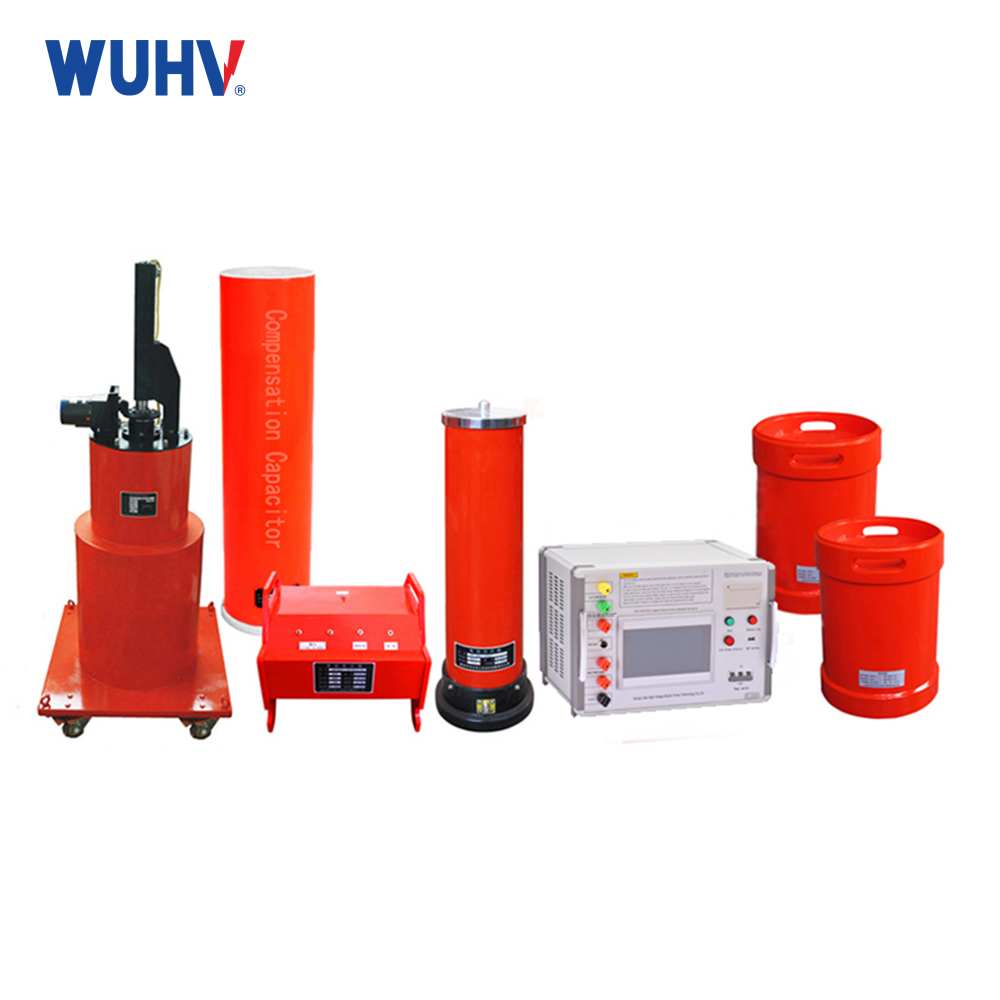
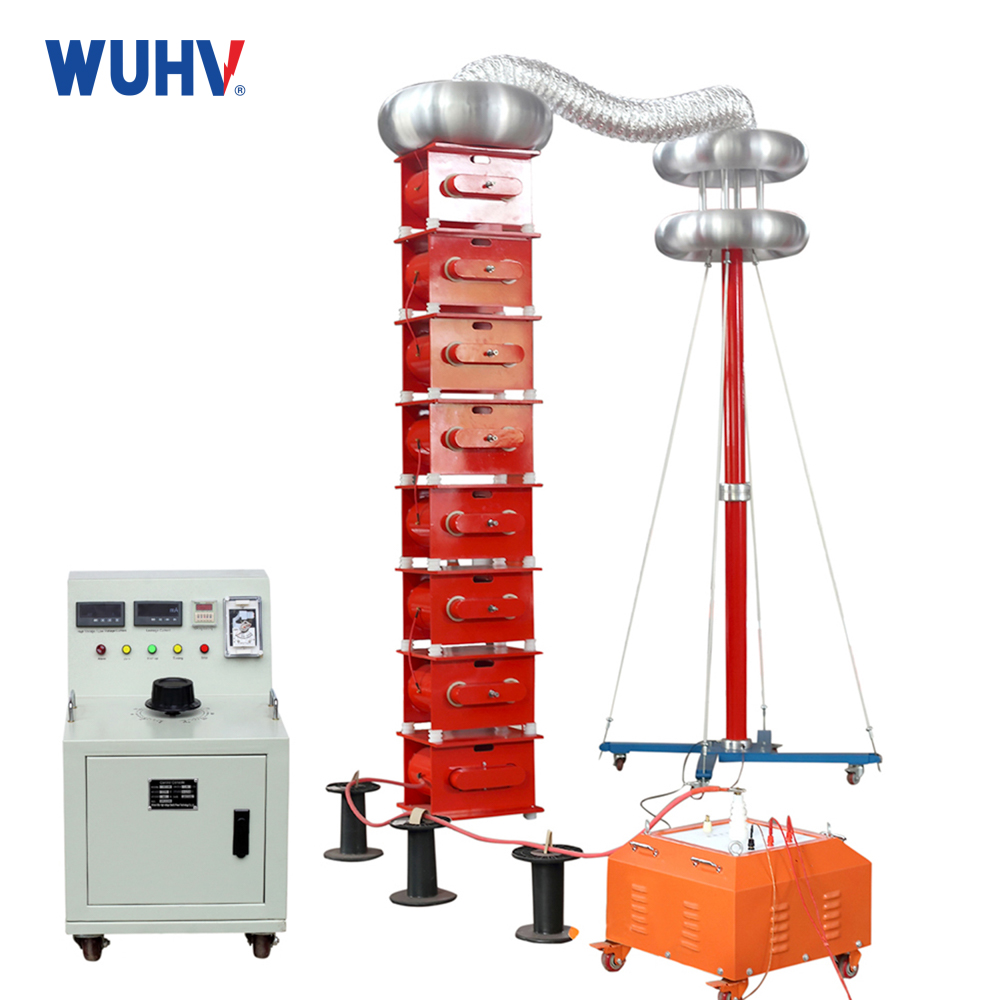
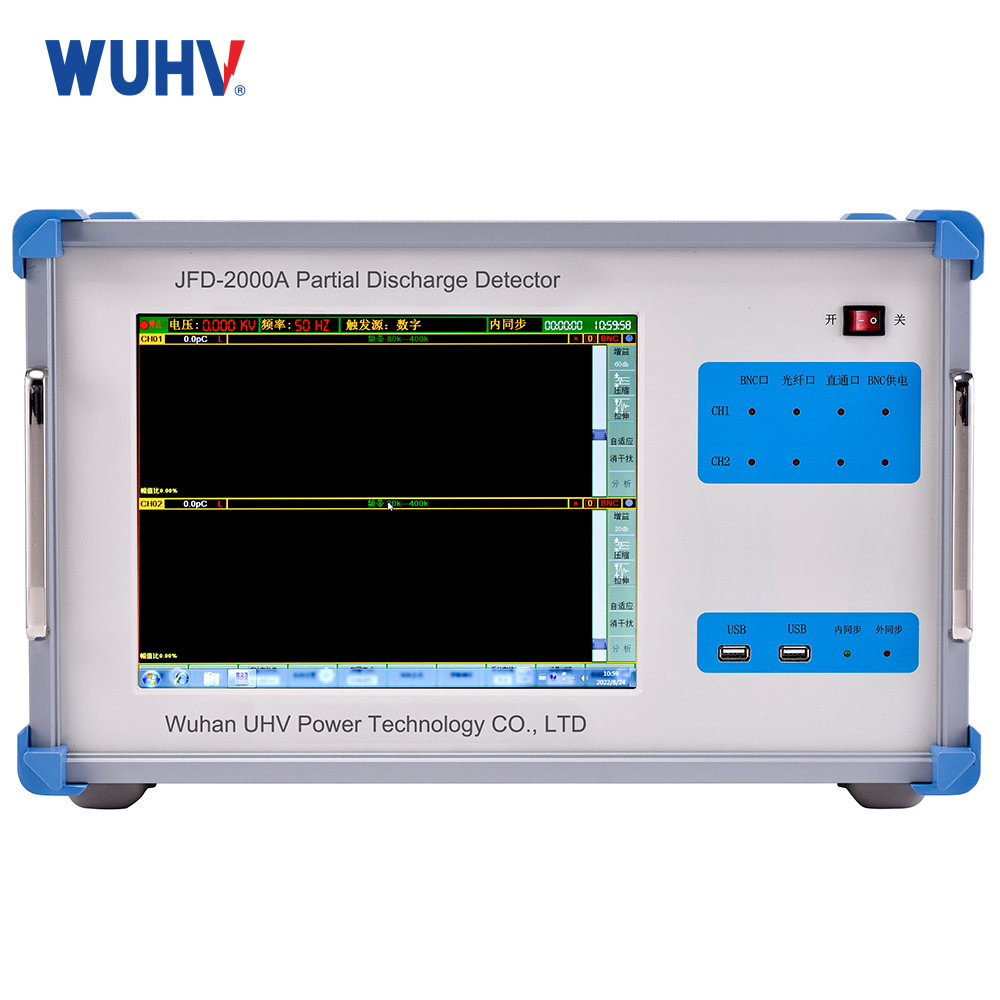
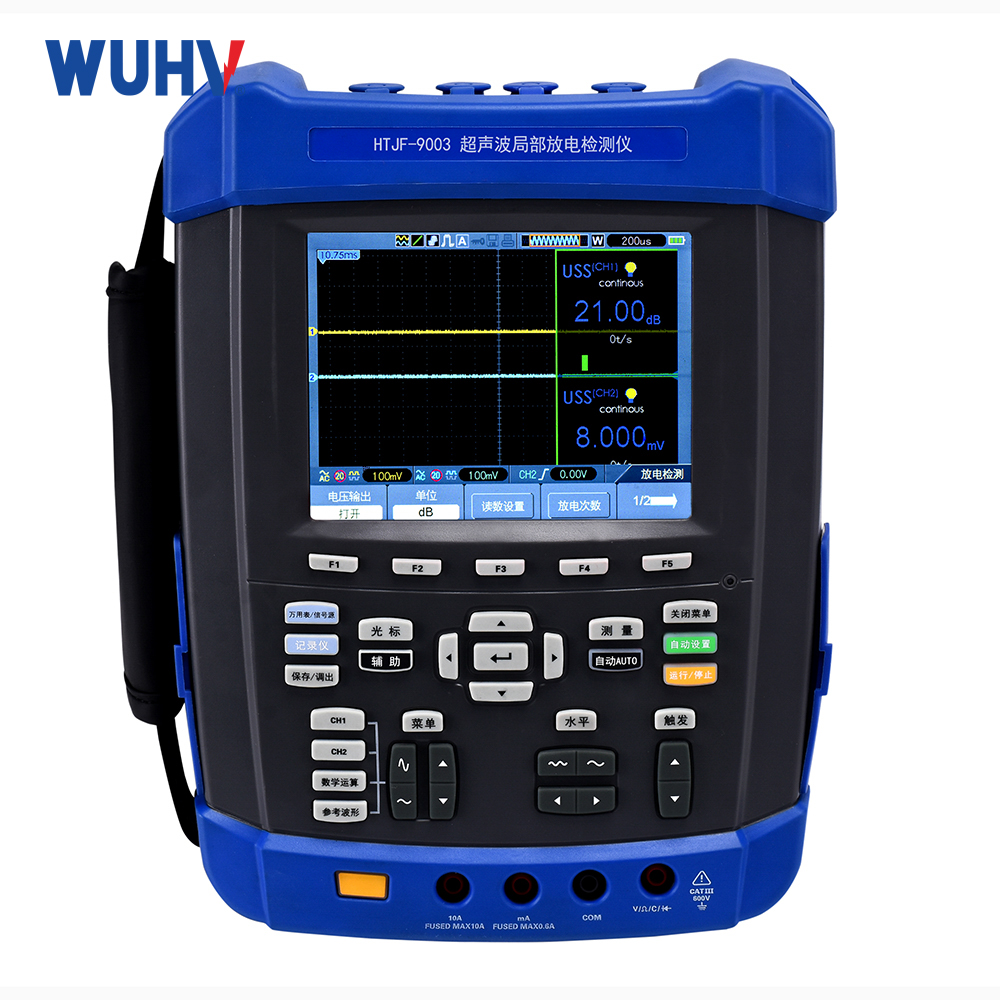
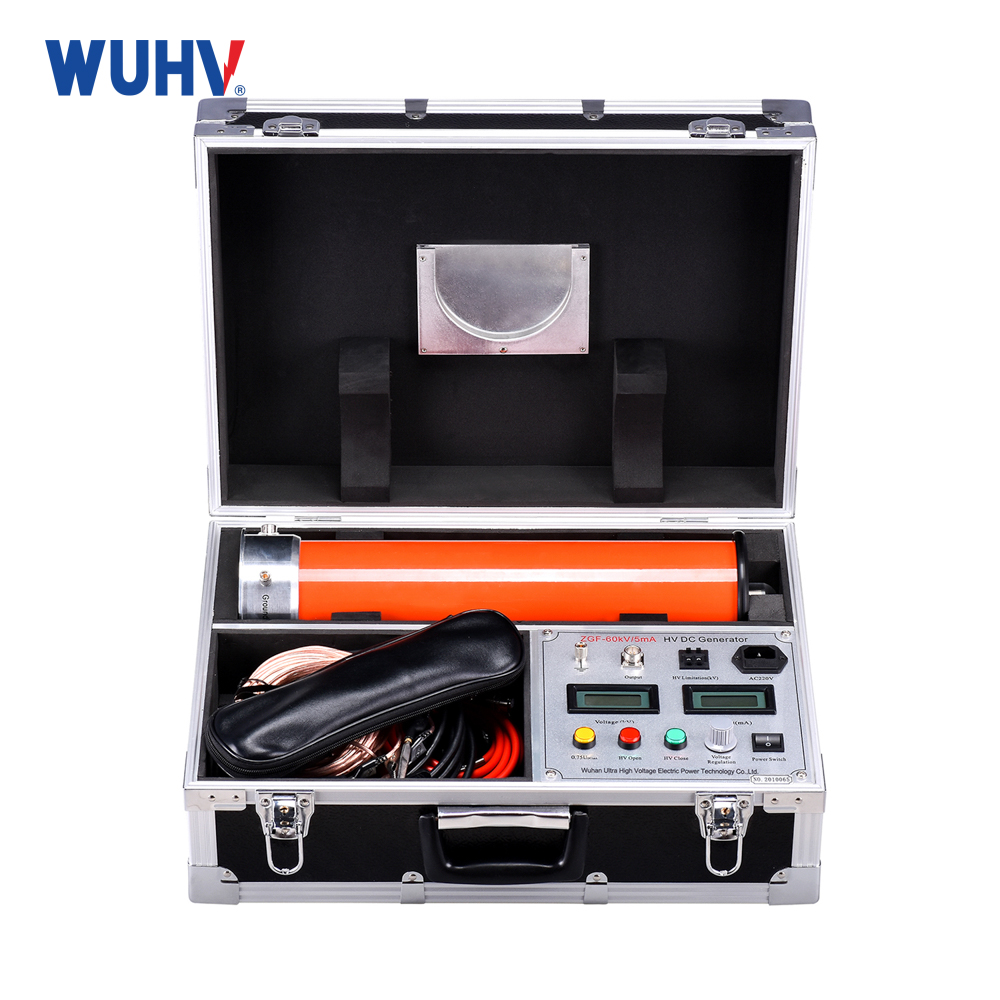
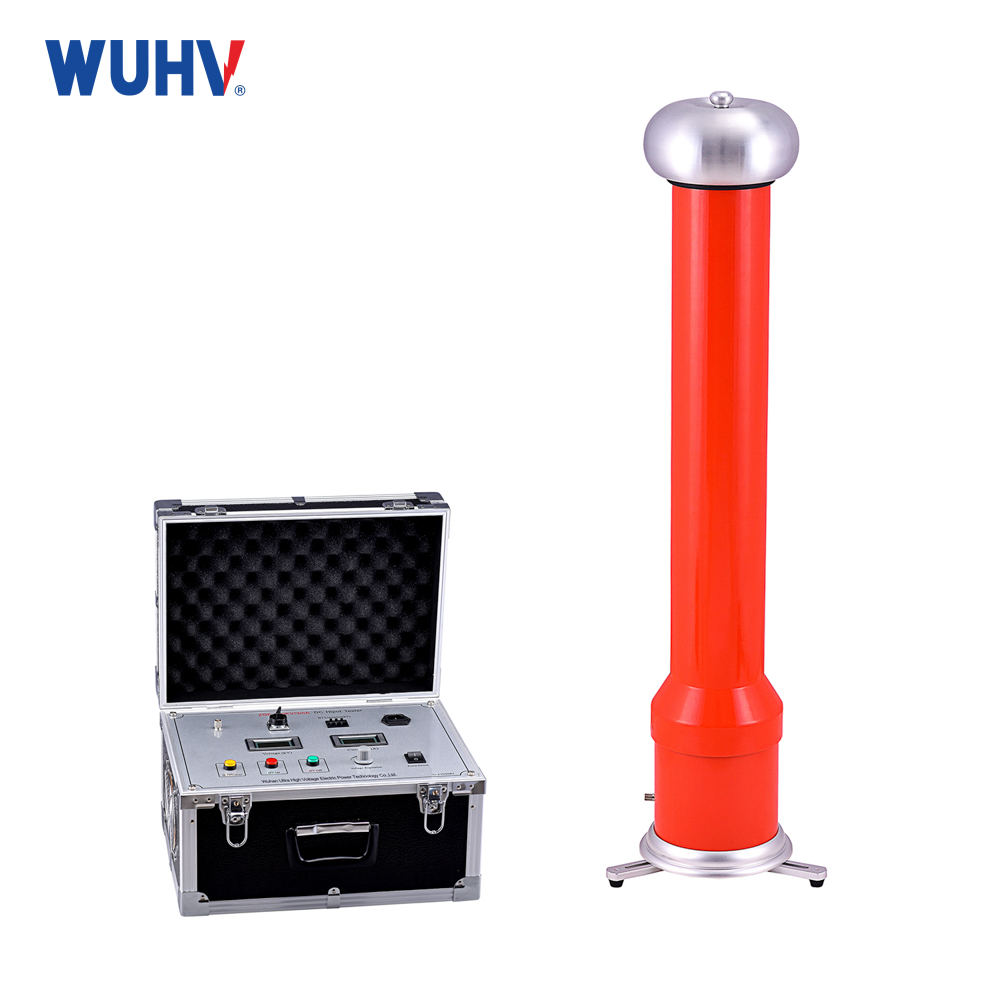
power cable fault tester? Wuhan UHV specializes in producingpower cable fault testerswith a wide range of product options. When looking for apower cable fault tester, choose Wuhan UHV.
At present, there are various types ofpower cable fault testerson the market, with prices ranging from several thousand yuan to several hundred thousand yuan, making it difficult for users to choose when purchasing such instruments. The materials, structures, uses, laying methods, voltage levels, and wiring methods of cables used in various industries are not the same. The common fault characteristics and solutions should also be different. At present, there are uneven manufacturers in the market, and few products can effectively solve various cable faults. The power cable fault tester developed by Wuhan UHV precisely solves various cable fault problems. Let's introduce them in detail below.
Working principle ofpower cable fault tester
The working principle of the power cable fault tester is that the power cable fault tester consists of three main parts: the power cable fault tester host, the cable fault locator, and the cable identifier. The main unit of the fault tester is used to measure the nature of cable faults, the total length, and the approximate position of the cable fault point from the testing end. The cable fault locator is used to determine the precise location of the cable fault point based on the approximate location determined by the cable fault tester host. For buried cables with unknown directions, a pathfinder is required to determine the underground direction of the cable.
The basic method for testingpower cable faultsis to apply high-voltage pulses to the faulty power cable, causing breakdown at the cable fault point. At the cable fault breakdown point, electromagnetic waves are generated and sound is simultaneously emitted while discharging. The working principle of the application of arc reflection method (secondary pulse method) in the positioning of power cable fault testers is as follows: first, a high voltage pulse of a certain voltage level and energy is applied to the fault cable at the testing end of the cable, causing breakdown and arc ignition at the high resistance fault point of the cable. At the same time, a low-voltage pulse for measurement is added to the testing end. When the measurement pulse reaches the high resistance fault point of the cable, it encounters an arc and reflects on the surface of the arc. Due to arc ignition, high resistance faults become instantaneous short-circuit faults, and low-voltage measurement pulses undergo significant impedance characteristic changes, resulting in the waveform of flashover measurement becoming a low-voltage pulse short-circuit waveform, making waveform discrimination particularly simple and clear. This is what we call the 'secondary pulse method'. The received low-voltage pulse reflection waveform is equivalent to a waveform of a wire core completely short circuited to ground. When the high-voltage pulse is released and the low-voltage pulse waveform obtained when the high-voltage pulse is not released are superimposed, the two waveforms will have a divergence point, which is the reflection waveform point of the fault point. This method combines low-voltage pulse method with high-voltage flashover technology, making it easier for testers to determine the location of the fault point. Compared with traditional testing methods, the advanced feature of the secondary pulse method is that it simplifies the complex waveform in the impulse high-voltage flashover method into the simplest low-voltage pulse short-circuit fault waveform, making it extremely easy to read and accurately calibrate the fault distance.
Thepower cable fault testerdesigned by Wuhan UHV is used for testing open circuit, short circuit, grounding, low resistance, high resistance flashover and high resistance leakage faults of power cables, as well as precise testing of open circuit and short circuit faults of coaxial communication cables and local telephone cables. It can also test cable paths, burial depths, radio wave speed measurement, determine cable lengths, and establish cable files for daily maintenance and management.